Glucose: understand its function and importance for the human body.
Glucose is a simple sugar that plays a key role in the functioning of the human body. This substance is the main source of energy for the cells of our body, especially the brain, heart and muscles. In addition, glucose is important for the proper functioning of the central nervous system and for maintaining the body’s metabolic balance.
Glucose is obtained through the digestion of carbohydrates present in the food we eat. When we eat, carbohydrates are broken down into smaller molecules and converted into glucose, which is absorbed into the bloodstream and transported to every cell in the body.
Proper regulation of blood glucose levels is essential for maintaining the health of the human body. Glucose levels that are too low can lead to symptoms such as dizziness, weakness and confusion, while levels that are too high can cause long-term damage to the body’s organs and tissues.
What is the function of glucose?
Glucose is one of the main sources of energy for the human body. It is used by the body’s cells to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the molecule responsible for providing energy for cellular activities. In this way, glucose is essential for carrying out basic body functions, such as breathing, blood circulation and maintaining body temperature.
In summary, glucose is essential for the proper functioning of the human body. It supplies energy to cells and is essential for maintaining the body’s metabolic balance. Therefore, it is important that blood glucose levels are properly regulated to ensure the individual’s health and well-being.
What happens to the body when glucose is high?
In summary, glucose is essential for the proper functioning of the human body and must be consumed in a balanced way to maintain good health. Consulting a doctor or nutritionist can help determine the amount of glucose each individual needs to maintain good health and quality of life.
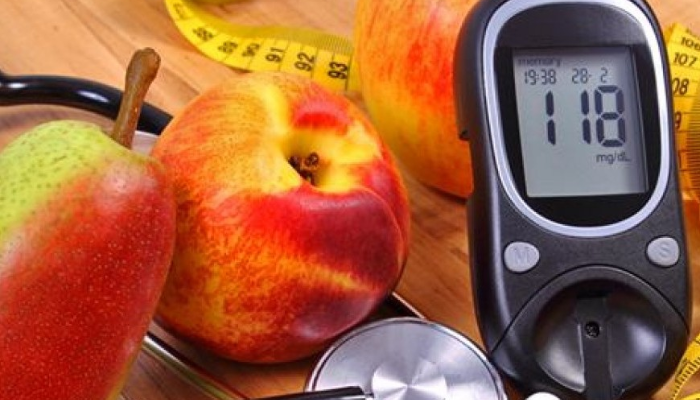
- Excessive thirst: When glucose levels are high, the body tries to eliminate excess sugar through the urine, which can lead to excessive fluid loss and, consequently, a constant feeling of thirst.
- Blurry vision: Hyperglycemia can affect the function of blood vessels in the eyes, leading to blurry vision.
- Fatigue: Glucose is the main source of energy for cells in the body, and when levels are high, glucose is not used efficiently, which can lead to a constant feeling of fatigue.
- Frequent infections: Hyperglycemia can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections.
- Kidney problems: High glucose levels can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to long-term kidney problems.
- Heart problems: Chronic hyperglycemia can increase the risk of heart conditions such as atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.
- Numbness or Tingling in the Hands and Feet: Chronic hyperglycemia can damage the peripheral nerves, leading to a feeling of numbness or tingling in the extremities of the body.
What causes increased glucose?
Increased blood glucose levels can be caused by several factors, the most common being poor nutrition. When we eat foods rich in simple carbohydrates, such as sweets, soft drinks and white bread, the sugar present in these foods is quickly absorbed by the body and raises blood glucose levels.
Another factor that can lead to increased glucose is lack of physical activity. When we don’t exercise regularly, our muscles don’t use glucose efficiently, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. In addition, stress can also contribute to increased glucose, as the body releases hormones that can raise blood sugar levels.
What to do to lower glucose?
Elevated blood glucose levels can lead to symptoms such as excessive thirst, increased urination, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. In the long term, it can cause complications such as neuropathy, kidney problems, retinopathy, cardiovascular problems and even amputations.
- Healthy Eating: Consume fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains, and avoid foods high in sugar and simple carbohydrates.
- Practice of physical activity: physical activity helps to reduce blood glucose levels, as muscle cells use glucose as a source of energy during exercise.
- Hydration: drink plenty of water to help the body eliminate excess sugar in the blood.
- Medications: In some cases, it may be necessary to use medications prescribed by the doctor to help reduce blood glucose.
- Stress management: Stress can raise blood glucose levels, so it’s important to find ways to manage stress, such as meditation, yoga, or other relaxing activities.
What is the difference between glucose and sugar?
Glucose and sugar are two different compounds, although they are related. Glucose is a type of simple sugar, also known as dextrose, which is produced naturally in the body and is used as an energy source by cells. It is found in foods such as fruits, honey and carbohydrates, which are digested and transformed into glucose in the body.
Another important difference between glucose and sugar is their impact on the body. Glucose is absorbed quickly by the body and is immediately used as an energy source by the cells, while sugar is absorbed more slowly and can cause blood sugar spikes. This can be especially problematic for people with diabetes, who need to carefully control their blood glucose levels.

Deixe um comentário